Global launch sequencing, once predictable, is potentially being reshaped by new Most Favored Nation dynamics and tighter pricing and reimbursement rules. To understand how companies are responding, Simon-Kucher interviewed 12 senior pharma and biotech leaders from the US and Europe – revealing how agility and foresight are now reshaping every decision.
The traditional model: An established practice with emerging limitations
For decades, pharmaceutical launches have followed a predictable geographic sequence, typically starting in the US before expanding to the EU4+UK, Japan, and other priority markets. Sequencing decisions mostly originate at the regulatory level, often 18–24 months before launch, guided by expected data readouts, regulatory and HTA review timelines, and dossier readiness. Commercial and P&MA teams generally entered the process later to review and refine the sequencing once pivotal data are available and filing plans are underway.
The rationale for this milestone-driven approach is twofold:
- To secure early revenue through rapid initial approval (often in the US).
- To establish commercial footprint and optimize international reference pricing (IRP) through a strategically planned and sequenced international product rollout.
Beyond geography, indication sequencing is equally critical to optimizing an asset’s long-term value. Companies typically coordinate country, and indication launches in tandem to manage pricing impact for future expansions. In oncology and rare diseases, early launches often target indications with high unmet need, strong clinical differentiation, and attractive price potential, frequently pursued through accelerated approval pathways to establish a firm initial price anchor. Lower-priced indications may then follow to preserve higher list prices and maintain favorable IRP positions. Chronic-disease portfolios tend to follow more traditional rollout patterns, reflecting larger patient populations and structured access frameworks. In ultra-rare diseases, sequencing can be less predictable, as patient advocacy, early-access programs, and national urgency often determine the order of launches.
Yet even within this “traditional” launch sequencing model, persistent challenges are evident. Responsibilities are often divided among regulatory, commercial, and access teams, leading to potential misalignment and unclear ownership of timing and priorities. Gaps in coordination during evidence planning can also disrupt international launch sequencing. When payer and HTA requirements surface late, companies may need to delay filings or adjust launch priorities to avoid negative assessments or unfavorable price impacts. International launch sequencing plans, once set, are rarely revisited even as market dynamics, competitive actions, or policy conditions evolve. Limited regulatory capacity and unclear governance processes can further create filing bottlenecks and slow decision-making, as global teams manage only a few submissions at a time and may lack clear escalation pathways when priorities conflict.
For many large pharmaceutical companies, the playbook remains unchanged: a structured yet rigid process built for a more predictable world. But the cracks are starting to show.
Traditional templates are too rigid for today’s HTA and pricing realities because they can’t keep pace with the volatility we’re facing.
The new reality: A volatile, polarized launch landscape
The assumptions that once guided global launch sequencing are now being tested by a policy and market landscape that is changing faster than many organizations can adapt. Market prioritization and launch sequencing now unfold against a backdrop of policy reform, divergent HTA standards, and emerging regional power centers.
Political and policy shifts
Several policy developments are reshaping the traditional global sequencing logic and prompting greater selectivity regarding where and when to launch.
- In the US, the emerging Most Favored Nation (MFN)-style pricing framework is increasingly reshaping global pricing expectations and launch sequencing considerations. Recent CMS proposals, most notably the GLOBE (Part B) and GUARD (Part D) models, introduce international price benchmarking into Medicare reimbursement and signal a more direct linkage between ex-US prices and US net pricing outcomes. In addition, the GENEROUS model for Medicaid further underscores growing cross-program pricing alignment and oversight. While these models are proposed and subject to ongoing policy and legal scrutiny, uncertainty around their long-term implications may prompt companies to delay or even forgo ex-US launches in certain countries to limit price exposure and risk.
- In the EU, the Joint Clinical Assessment (JCA) introduces shared evidence packages and synchronized HTA submissions that, while adding new coordination layers and adding near-term complexity for traditional early-launch markets, are expected to accelerate access in later-launch markets by allowing them to rely on a unified EU HTA dossier. Ultimately this will drive greater long-term alignment and efficiency across Europe. These dynamics will increasingly intersect with the forthcoming EU Pharmaceutical Legislation Reform, which signals a substantial regulatory recalibration through revised data protection and market exclusivity rules, new launch-availability obligations, shorter EMA timelines, and expanded transparency requirements. Uncertainties on operationalization and implications remain however.
- In the UK, strict cost-effectiveness thresholds and VPAG payback requirements have made early UK launch less attractive in recent years, as companies reassess trade-offs between fast UK access and a high visible list price versus lower (confidential) net price potential. However, recent policy commitments to raise baseline ICER thresholds (by 17-25%) and reduce VPAG repayment rates (to 14.5%) may help sustain the UK’s role as an important early launch market.
- In Japan, ongoing drug pricing reforms reflect a dual focus on fiscal discipline through annual price revisions and innovation incentives via the Rapid Launch Premium and Price Maintenance Premium programs. Continued policy discussions are closely monitored for their potential impact on price predictability.
- In China, even though the country’s sheer market scale is reinforcing its long-term strategic importance, annual NRDL updates, price renegotiations and increasingly steep reductions pressure profitability and push companies to diversify market access strategies by expanding self-pay and private/commercial health insurance channels alongside the NRDL pathway.
These shifts are pushing companies to recalibrate launch strategies and narrow their focus to markets that balance speed, price sustainability, and long-term value realization.
Companies are becoming far more selective, focusing on a smaller set of priority markets that account for the majority of global revenue.
Economic and structural dynamics
A set of economic and structural forces is also influencing launch decisions, from shifting conditions in established regions to the growing relevance of emerging markets:
- Germany remains a preferred first-wave market due to immediate launch access, but tougher post-launch renegotiations have eroded its early revenue advantage, placing it among the three European countries with the lowest list prices for 44% of new drugs introduced since 2023. New confidential net discounts introduced in January 2025 under the Medical Research Act (Medizinforschungsgesetz, MFG) and Germany’s key role as a reference market within ongoing US MFN-style policy discussions may further influence global launch prioritization and future US price anchors.
- France faces longer HTA timelines, reflecting a trend of increasingly stringent value assessments delaying market entry.
- Japan and China are expected to continue requiring more localized evidence to satisfy evolving regulatory and reimbursement expectations.
- Emerging markets, such as Brazil, the GCC, and select APAC countries, are gaining importance, especially in oncology, rare diseases, and other high-value specialty indications, supported by targeted opportunities for faster access, e.g., participation in Project Orbis, which enables concurrent FDA-partner reviews and allows markets like Brazil and Singapore to achieve materially shorter approval timelines, alongside growing and often younger patient populations, and, in some cases, greater pricing flexibility.
Global teams must now recognize how launch decisions in one market affect outcomes elsewhere. Tightening IRP linkages, evolving MFN dynamics, and broader economic and structural shifts are deepening cross-market dependencies, heightening policy spillovers, and amplifying both revenue and reputational risks tied to differential access.
In addition, there is a growing need for fully integrated, cross-functional launch teams that operate beyond traditional silos. With sequencing now as much about risk-management as commercialization, close coordination across pricing, access, commercial, and regulatory functions is critical.
How the industry is evolving: Inside the transition
Even before recent policy and market disruptions, many pharmaceutical companies had begun re-engineering launch sequencing to address internal inefficiencies and cross-functional gaps. What started as an effort to improve coordination and accelerate decision-making is now reinforced by external pressures, most notably the global implications of MFN on European price referencing, confidential discount structures, and cross-market access timing.
This transition is unfolding along five key dimensions:
- New coordination models: Many companies have been coordinating via Launch Sequencing Councils or cross-functional teams that co-own international sequencing decisions across Regulatory, Commercial, and P&MA. This shift is supported by RACI matrices, escalation rules, and capacity calendars that prevent bottlenecks and increase transparency between functions in decision-making.
- Earlier integration of clinical development: There is a clear shift toward aligning sequencing with commercial and P&MA priorities earlier in clinical development. Companies are incorporating strategically important geographies into pivotal trials and tailoring trial design – for example, by selecting relevant comparators or endpoints. Local trial participation not only helps meet HTA expectations, but also strengthens launch readiness, as early clinician exposure builds confidence and accelerates post-approval uptake. China’s growing strategic importance and innovative R&D ecosystem have increased its presence in multi-regional clinical trials for pipeline assets.
- Analytical capability and scenario planning: Companies are deploying scenario engines to model MFN exposure, IRP chains, competitor timelines, and policy risk, enabling them to test alternative international rollout paths under uncertainty. The shift from precedent-based sequencing toward data-driven optimization reflects the growing volatility of the evolving external environment.
Scenario planning is constant. We maintain a most-likely and a fallback scenario, and re-evaluate them as data, competitors, or regulators shift.
- Market configuration and alignment: Regional market clustering, such as DE-AT-CH, GCC, BR-MX, Nordics, UK-IE, helps streamline filings and optimize resources, particularly among smaller organizations. The JCA framework in Europe illustrates how aligned evidence requirements can improve efficiency and enable coordinated cross-market approaches. Many companies are also introducing tiered pricing frameworks alongside launch sequencing to maintain consistency within clusters while broadening patient access. At the same time, MFN-related pricing pressures are also prompting a rebalancing between core and secondary markets, with more deliberate management of pricing exposure and, in some cases, significantly more cautious rollouts despite potential cluster-related efficiency gains.
- Operational readiness: Clinical trial infrastructure, local manufacturing and distribution capabilities, pursuit of early-access pathways, and supply assurance now determine market prioritization. Some companies treat these operational elements as hard go/no-go criteria.
International commercialization and launch sequencing strategies vary by company size. Large pharmaceutical players typically benefit from broad infrastructure but often face slower governance, while biotechs rely on tighter launch clusters, more disciplined capital allocation, and partnership-driven models. Approaches also differ by therapy area: Many organizations are formalizing TA-specific frameworks, recognizing that one model no longer fits all, particularly given MFN-linked deals, accelerated launches in oncology and rare diseases, and heightened price sensitivity in chronic conditions.
Overall, a broader transition is underway in the industry – still anchored in traditional markets, but increasingly dynamic, iterative, and risk balanced.
The path forward: Opportunities for a future-ready launch sequencing strategy
Next-generation launch sequencing is shifting from static calendars to living, adaptive systems that are continuously updated, data-enabled, and jointly owned across functions.
Commercial process agility
Future launch excellence is expected to move beyond the rigid “US + priority markets first (EU4, UK, Japan)” sequence. Companies are shifting toward flexible, situation-specific launch clusters that balance speed, evidence generation, and IRP exposure according to each asset and market context. Agility in governance will be essential to enable differentiated commercialization approaches across therapy areas, allowing companies to adjust sequencing as conditions evolve.
From alignment to anticipation
The next leap forward may come from anticipating policy and pricing shifts before they actually materialize. As Most Favored Nation clauses and other pricing reforms reshape global launch priorities, some organizations are beginning to use scenario modeling and cross-market simulations earlier in planning to inform regulatory and commercial choices. The EU JCA and tightening national value frameworks may further prompt companies to reconsider how they cluster markets and sequence submissions across Europe. Success will depend on developing policy foresight as a strategic capability, supported by closer collaboration with policymakers around confidential pricing, value-based access, and outcome-linked reimbursement.
AI-enabled launch intelligence
Forward-looking organizations are already exploring AI-driven sequencing engines that integrate IRP chains, MFN exposure, HTA timelines, and competitor activity into unified decision-support environments. These systems have the potential to transform sequencing from a periodic planning exercise into a continuously optimized, real-time process.
AI tools can help us stay flexible and adapt launch sequencing in real time.
Reframing launch excellence
For launch excellence to succeed in an increasingly volatile political, economic, and structural climate, it demands a move from defensive sequencing toward a more strategic capability that delivers lasting value. In the decade ahead, success will depend less on long-standing, traditional launch patterns and predefined templates, and more on intelligent, agile sequencing models that combine policy foresight, earlier cross-functional coordination, and data-driven flexibility to shape global commercialization strategies. Ultimately, the ability to anticipate, adapt, and act with agility in international launch sequencing may distinguish tomorrow’s leaders from those left behind.
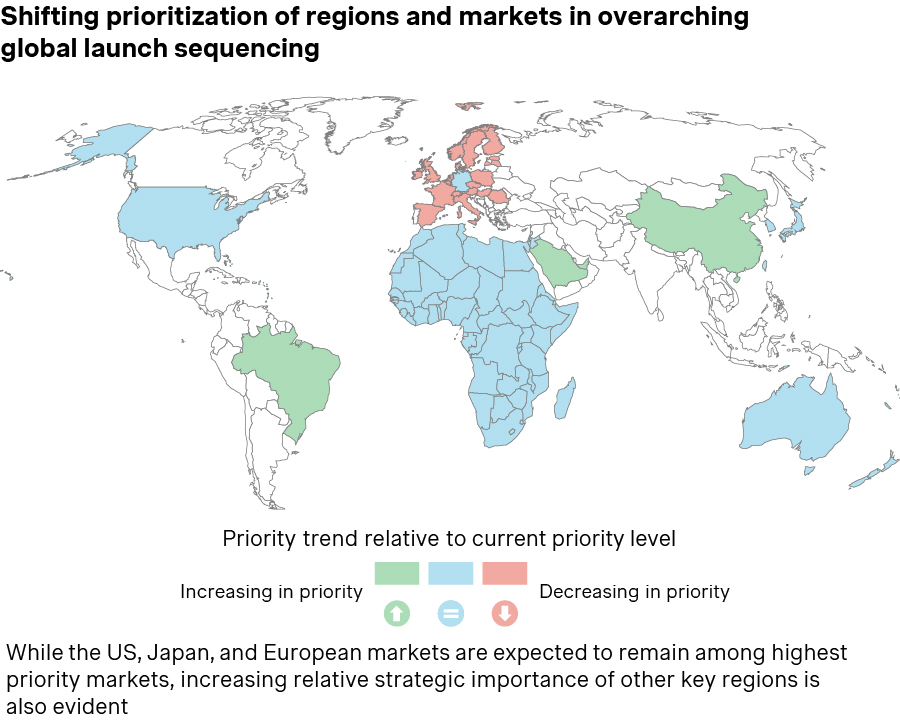
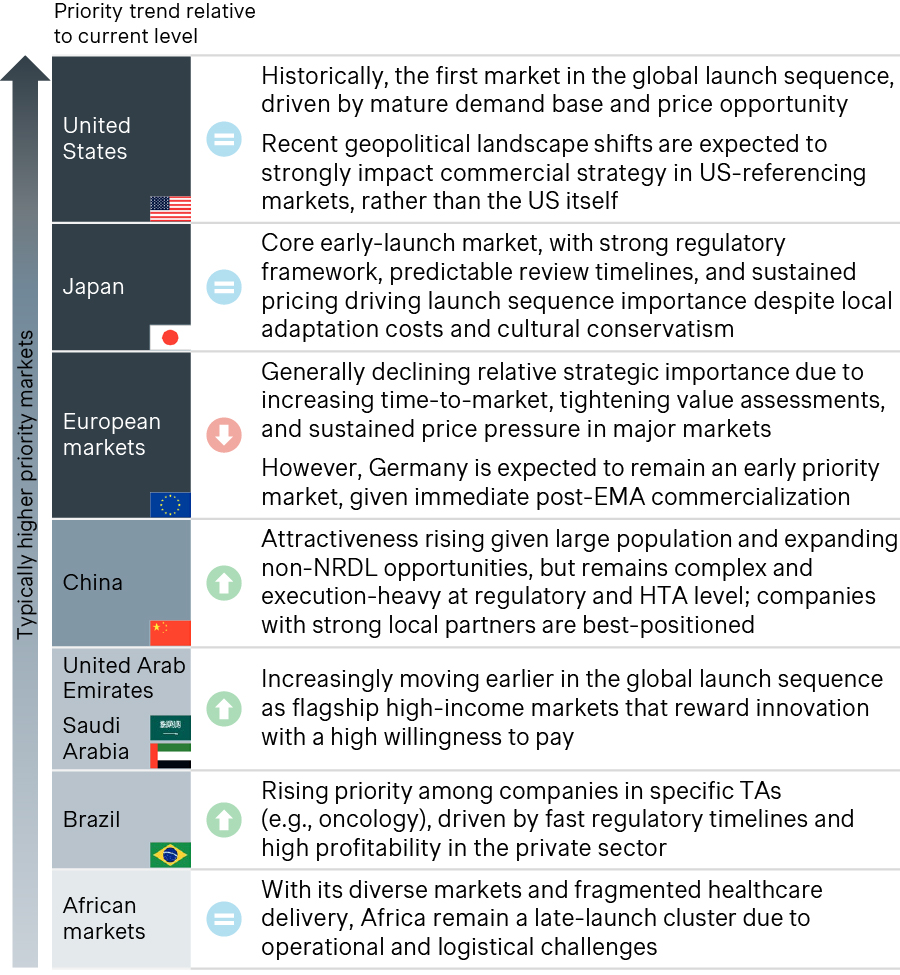
Source: Simon-Kucher; EU: European Union; GCC: Gulf Cooperation Council; MFN: Most Favored Nation; UAE: United Arab Emirates; US: United States
Thanks to contributions from Mia Hofmann!
Mitigate the impact of international reference pricing with LS Genius| IRP, an advanced AI-based software that helps you to navigate IRP complexity and optimize cross-country and launch sequence strategies.



