Tenders are becoming increasingly relevant for purchasing in the healthcare sector, particularly for established products at the mature stage of the product lifecycle. To ensure profitable growth, pharmaceutical companies need to strive for tender management excellence. In this article, we focus on successful tender strategy and execution.
Procurement through tenders has become a key lever for cost containment in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the evolving healthcare landscape, tendering (i.e. competitive bidding between potential suppliers for a particular contract) is becoming more important to pharmaceutical companies when their products reach the mature stages of their lifecycle. Companies need adapt to the shift from clinical selling toward tendering as the new standard procurement practice in a competitive environment for the established part of their portfolio.
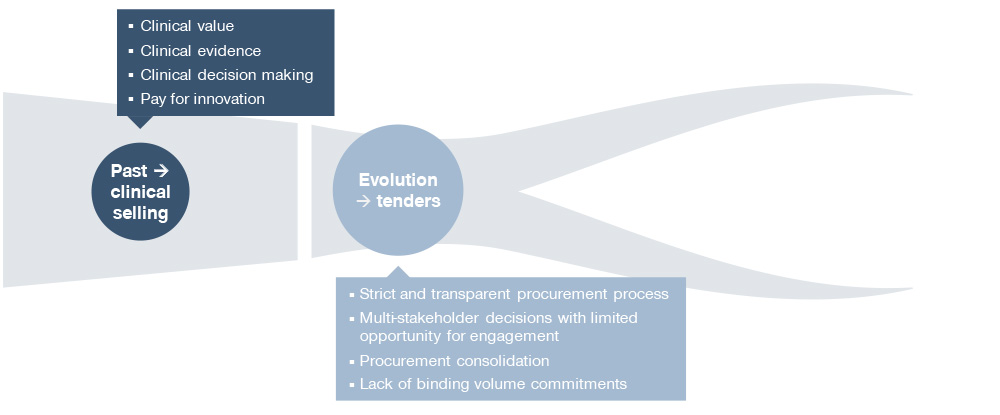
In theory, tendering looks quite simple: high transparency, price as the most important decision criterion, no engagement with stakeholders, and standardized processes. However, in reality, pharmaceutical companies have to deal with multiple stakeholder involvement, limited stakeholder access, and varying processes across markets. Considerable country-specific differences in tender specifications (e.g. price-focused vs. value-oriented) require tender strategy and execution to be localized. Furthermore, the tender structure needs to be carefully analyzed to capture relevant differentiation opportunities on the product level and beyond.
Tender challenges and opportunities
The evolution of procurement within tenders poses various challenges but also provides new opportunities:
 |
|
 |
|
Our project experience shows that a poor tender strategy can have a significant impact on overall business performance. In many cases, while volume increases, profitability drops over the long term and market prices generally erode. Pharmaceutical companies need to follow a structured, proactive approach to secure volume and avoid being trapped in a continuous price erosion cycle.
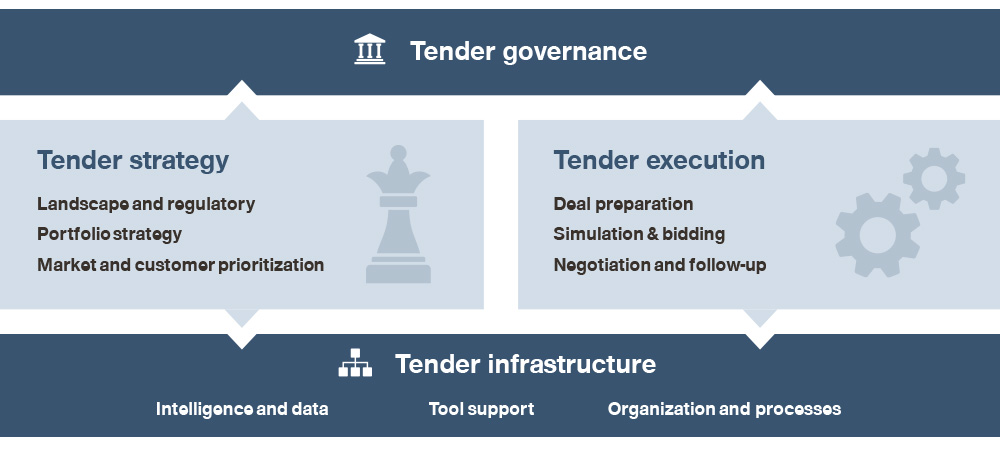
Supporting top pharma companies in their tender management efforts for many years helped us to develop a four-part framework guiding to tender excellence: Tender governance defines key guidelines in order to steer tender performance across the organization. Tender infrastructure sets up the necessary foundations for successful tender implementation. Tender strategy takes the current procurement landscape for pharmaceuticals into consideration and focuses on tender prioritization while tender execution describes the process from deal preparation to tender bidding up to post-tender engagement.
Tender strategy: Portfolio considerations and tender prioritization
The first basic requirement for an effective tender strategy is in-depth knowledge of the market conditions and main tender archetypes and awareness of possible regulatory changes that could affect your business. The second is understanding available differentiation options within the portfolio and developing a product offering tailored to customers’ needs. The goal should always be to maximize value differentiation opportunities for each tender type and improve the tender body’s perception of the differential value of their offering’s differential value in terms of importance and performance:
- Which drivers are considered in a purchasing decision for your type of product and how relevant are they for the decision?
- Based on that, which criteria make you stand out from the competitors (i.e. what is your competitive position)?
- How can you use marketing materials and tools to increase the relevance of differentiation criteria?
This value-oriented approach provides a clear indication of price premium potential for winning the tender. If value-based differentiation isn’t deemed sufficient, company-related or value-added services can be added, e.g. in terms of smart packaging, flexible delivery times, or product training sessions.
Answering these basic questions sets the strategic direction for tender prioritization. Which must-win tenders should be prioritized? Companies should focus tender efforts and execution on attractive tender archetypes according to their differential value position to drive win-loss and price opportunity. No single company ever deserves 100 percent of the market share, so you need to target the most promising deals out there and maximize your efforts and engagement toward your prioritized deal types. As soon as this is done, you can develop an individual tender strategy and execution plan and define goals for each tender type.
Tender execution: Deal preparation and submission process
The key to successful tender management is having a good execution concept that fits your strategy. There are three phases in tender execution: pre-tender, live tender (tender submission), and post-tender. In each phase, you need to consider external engagement and internal processes. Tender success is mainly driven through customer engagement prior to tender publication.
Understanding the stakeholder landscape and access is mission-critical to securing successful pre-tender engagement. At this stage, pharmaceutical companies need to consider external engagement to educate customers on the differential value of their offering and structural tender elements (e.g. lot definition, specification inclusion, scoring mechanisms), and drive internal tender processes (e.g. intelligence and data collection, bidding simulation and wargaming, negotiation preparation).
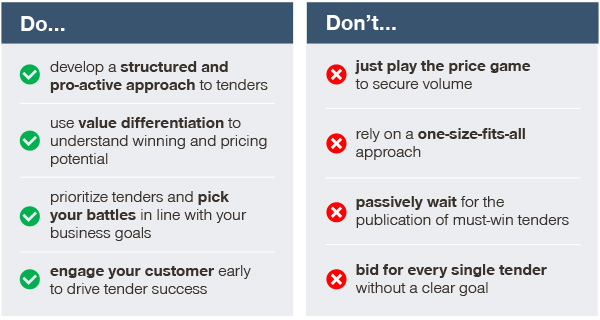
Dos and don’ts of tender strategy and execution
Intelligent tender strategy and execution are essential parts of successful tender management. The following dos and don’ts sum up the most important lessons learned:
Conclusion: Tender strategy and execution are only one part of the puzzle
As tendering has become the new standard procurement practice, pharmaceutical companies must take their tender strategy and execution to the next level in order to secure profitable growth in an increasingly competitive environment. Investing in tender excellence will yield significant return managing product commercialization and product life cycles effectively. Applying a structured tender excellence framework and combining central steering with local execution will drive impact and secure success.








