What key pricing and market access (P&MA) developments should pharma leaders address today? How can you respond with confidence and steer your organization toward long-term advantage?
It is a new era for pharmaceutical P&MA. From policy reforms to digital advancements, these global and regional developments are shaping how pharmaceutical companies are engaging with their partners.
Yet, many organizations are still unprepared for these shifts, risking missed opportunities and long-term challenges. Through discussions with industry leaders, we have identified four critical developments impacting the P&MA function across the industry:
- Harnessing generative Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Advancing Real-World Evidence (RWE) strategies
- Navigating the European Joint Clinical Assessment (EU JCA)
- Addressing market access challenges in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs)
In this article, we explore the implications of these market trends and offer guidance for P&MA leaders on how to:
- Enhance the P&MA organization
- Optimize P&MA operations
- Build the P&MA capabilities needed for growth
Drawing on Simon-Kucher's Pricing & Market Access Excellence framework, we outline how P&MA leaders can prepare for the future by strengthening organization, operations, and capabilities.
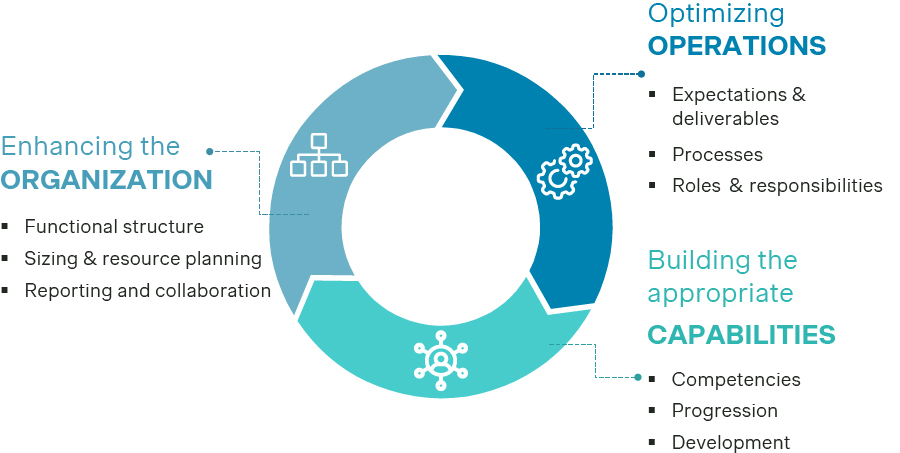
The four pricing and market access trends highlighted in this article should be prioritized by every pharmaceutical and biotech company, though they are by no means exhaustive. P&MA leaders must stay alert to additional, country-specific developments that impact local strategies (e.g., US IRA).
Development 1: Harnessing generative AI for the P&MA function
Initially perceived as a buzzword, generative AI now represents a game-changing opportunity for P&MA. A solid technical infrastructure is essential for any AI initiative, as without it, projects stall or fail due to insufficient data foundations. Here, we assume this basis is in place and focus on the organizational, operational, and capability requirements needed to leverage AI in P&MA.
Enhancing the organization: Establishing AI leadership in P&MA
Many P&MA teams lack dedicated AI roles. To harness AI's potential, leading organizations should:
- Create a dedicated team: Build a team with both strategic and operational expertise to lead P&MA AI initiatives (e.g., defining optimal country launch strategies for International Reference Pricing).
- Prioritize high-impact initiatives: Focus available resources on high-priority P&MA AI initiatives with measurable outcomes (e.g., collecting information from guidelines and using HTA decisions as input for PICO prediction relevant for EU JCA).
- Align with company strategy: Strengthen reporting and collaboration by aligning P&MA AI initiatives with broader company strategies to drive business objectives.
Optimizing operations: Identifying the right AI use cases while addressing limitations in prediction and calibration
P&MA in pharmaceutical and biotech companies can use generative AI to predict outcomes, prioritize strategies, and streamline time-intensive tasks. However, effective use requires a structured approach to identifying where AI delivers the most value.
Predicting P&MA-related outcomes | Prioritizing P&MA strategies leveraging historical data | Streamlining time-intensive tasks |
|
|
|
Building capabilities: Ensuring foundational AI knowledge for all and specialized expertise for a few
Most pharmaceutical and biotech companies have not integrated AI into P&MA trainings. To close this gap, organizations should:
- Develop foundational AI knowledge: Integrate AI literacy into existing trainings to ensure teams understand key concepts such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and relevant P&MA use cases (e.g., using historical data to assess the impact of trial design on market access outcomes).
- Build specialized AI expertise: Upskill select team members to lead AI-driven P&MA initiatives, providing advanced training (e.g., leveraging AI-powered tools or large language models for literature reviews and competitive analysis).
Development 2: Empowering the P&MA function to enhance RWE generation
Leading pharmaceutical and biotech companies are adopting RWE strategies to address pressure on R&D efficiency, shifting regulatory expectations, and increasingly rigorous clinical assessments. For P&MA, RWE is critical in overcoming challenges such as payer evidence gaps, shaping contracting strategies, and supporting reimbursement. This is particularly relevant as payers begin to re-evaluate launch decisions to ensure real-world value aligns with initial claims.
Enhancing the organization: Integrating P&MA perspective to ensure impactful RWE generation
Many companies lack a holistic approach to RWE. There is significant variability in how it is managed, with some organizations assigning it to the Medical team, while others place it under HEOR or P&MA. In some cases, responsibilities are shared across multiple functions. While some organizations are closely aligned with P&MA, others show limited integration. This fragmented approach can hinder the development of effective, payer-focused RWE strategies throughout the asset lifecycle. Embedding RWE into integrated evidence planning within P&MA enables earlier payer alignment and strengthens market access strategies.
Developing RWE strategies involves collaboration across HEOR, Clinical, Medical, Regulatory, P&MA, and Commercial teams, each with specific roles (e.g., Clinical focuses on R&D and Regulatory on approvals, P&MA on payer evidence, and Commercial on HCP engagement). Despite serving different "customers," alignment is critical to developing a cohesive RWE strategy. The goal is to fully integrate RWE into each asset's evidence profiles. This enables early assessment of RWE-generation options to optimize pricing and market access.
Optimizing operations: Shifting RWE from fulfilling purely clinical needs to also addressing P&MA strategic objectives
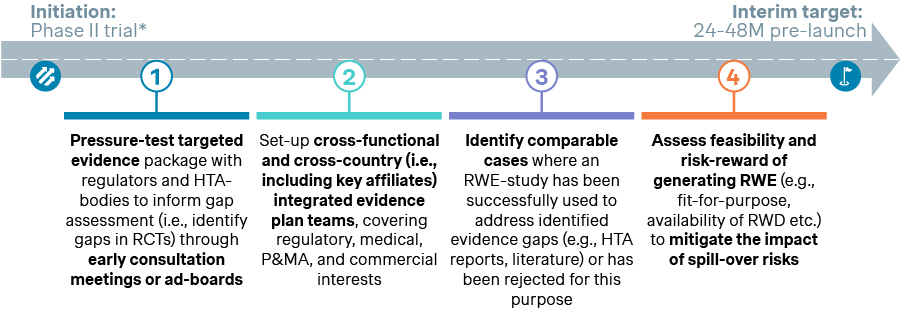
We have seen RWE evolve from primarily supporting medical and regulatory goals to being fully integrated into P&MA objectives. To achieve this, leading companies employ a four-step process that starts as early as Phase II with interim targets set 24-48 months before launch. These steps, illustrated below, ensure early alignment with P&MA objectives:
Building capabilities: Upskilling local P&MA teams on RWE strategies and core concepts
While company-wide RWE capabilities are essential, many local P&MA teams still struggle to interpret and communicate RWE effectively. Compared to randomized controlled trials, RWE requires a broader range of data, including patient-reported outcomes and healthcare resource utilization. Without focused upskilling and practical support, local teams may lack the ability to use RWE insights in a way that resonates with P&MA stakeholders.
To maximize the value of RWE in P&MA strategies, top-tier companies implement structured training and foster continuous knowledge-sharing for local teams, including:
- Bite-sized knowledge development, e.g., building storyline pieces and concepts relevant to the RWE study program through engaging formats.
- E-learning week and Q&A sessions, e.g., offering short, interactive formats with global Medical/HEOR teams to explain complex strategies and encourage real-time dialogue.
- Comprehensive e-learning platform, e.g., providing on-demand access to training materials leveraging internal knowledge hub to ensure easy, self-paced learning.
Development 3: Navigating the European Joint Clinical Assessment (EU JCA)
The EU JCA is reshaping pharmaceutical P&MA in Europe. As of January 2025, oncology treatments and advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) must undergo joint clinical assessment. This requirement will expand to orphan drugs by 2028 and to all medicines by 2030. It creates a more complex landscape with a new external stakeholder that companies must plan for. Pharmaceutical and biotech companies must stay agile while navigating this change.
Enhancing the organization: Adapting to a new "customer"
To meet the new JCA requirements, successful pharmaceutical and biotech companies are appointing above-brand EU JCA leads to ensure organizational readiness. These responsibilities shift to brand Market Access and HEOR teams as assets approach pre-launch readiness and require product-specific strategies to be developed.
While other functions remain largely unchanged structurally, the JCA introduces a new external stakeholder that companies must actively engage. This is prompting earlier and more sustained cross-functional collaboration across Regulatory, Medical, Access, HEOR, Clinical, and Policy teams. EU JCA requirements are being embedded into key clinical development decisions to ensure alignment with the expected scope and rigor of the JCA. Strategy development is typically led by Access and HEOR teams, with final sign-off integrated into clinical trial design milestones.
The EU JCA is also pushing companies to rethink resource planning. New roles, such as above-brand EU JCA leads, are being created. Most functions are trying to absorb these new responsibilities alongside core roles, but some under-resourced teams are requesting additional headcount to stay ready. For instance, Product Access and HEOR teams often integrate JCA responsibilities into existing responsibilities. Across organizations, the greatest increase in resource needs is for additional indirect treatment comparison studies – essential for generating evidence for each potential PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) scenario under the EU JCA process.
Optimizing operations: Integrating EU JCA deliverables into launch readiness
Preparing for EU JCA requires creating new deliverables and integrating new evidentiary requirements into the existing launch readiness process. Considering the timeline, key deliverables should be developed on an ongoing basis throughout the asset development stages, starting before pivotal trial lock-in and extending through to post-JCA report endorsement.
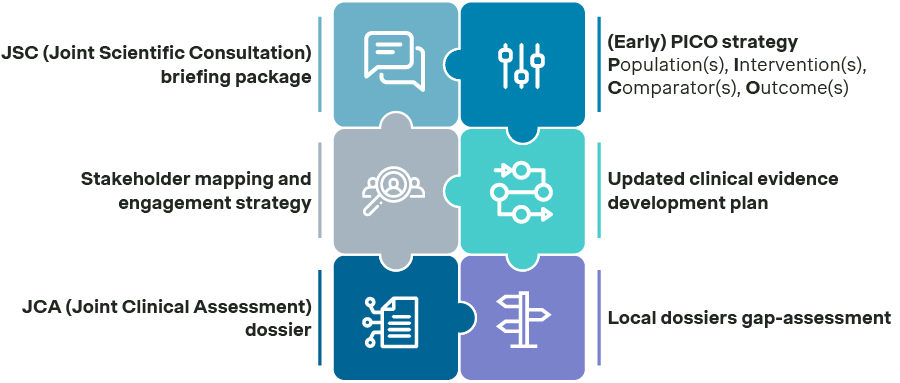
Building capabilities: Empowering the entire organization for EU JCA success
Understanding EU HTA requirements and preparing key functions is essential for EU JCA readiness. Global, regional, and local P&MA stakeholders must stay current on the emerging EU JCA and local payer policies to ensure that strategies reflect the changing policy landscape. Timely communication is key, particularly regarding country-level payer guidance. As many payers have yet to release final guidance, timely updates help maintain consistent readiness and close knowledge gaps across functions.
Communication should be tailored by function, role, and seniority. By combining targeted communication, smart tools, and structured training, companies can build the capabilities needed to successfully manage the EU JCA process.
Explore our EU JCA resource center, including our EU HTA project offerings related to organizational excellence
Development 4: Addressing market access challenges in LMICs
Today, healthcare realities in LMICs demand that pharmaceutical and biotech companies shift from a philanthropic model to a strategic, business-driven approach. Home to 85% of the world's population, these regions are seeing a rapid transformation in healthcare, driven by increasing life expectancy, rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs), and a growing middle-income patient segment. Despite challenges like market access complexities and budget constraints, there are significant P&MA opportunities emerging from expanding access and a changing affordability profile.
Adapting the organization: Bridging global/regional strategy and local execution
Two common pitfalls limit success in LMICs: global and regional teams imposing a one-size-fits-all P&MA strategy, and local teams operating independently and disconnected from global or regional leadership. This results in inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Successful companies encourage collaboration between global, regional, and local teams to support long-term strategy. While local teams bring valuable insight - possessing deep knowledge of the market ecosystem, including regulators, key opinion leaders, and P&MA stakeholders - strategic guidance should remain at the global or regional level.
Defining the optimal structure of local P&MA teams is also crucial. In many LMICs, a small team, or even a single individual, may oversee multiple markets and handle responsibilities beyond pricing and market access. Depending on the market and business priorities, companies may choose to:
- Establish a local team with in-house P&MA capabilities among others.
- Adopt a hybrid model, keeping strategic P&MA in-house but outsourcing commercialization.
- Rely on external partners, leveraging third-party expertise for market entry.
Selecting the right external partners is also critical. Companies must prioritize those with deep therapeutic expertise, strong supply chain reliability, and relationships across the local healthcare ecosystem, including clinicians, public payers, and private insurers. Success depends not just on selecting the right partner but also creating agreements that reflect local market realities and support long-term P&MA strategy. For example, while local partners may push for lower prices to drive volume, companies must balance pricing models to sustain market access and support global objectives.
Optimizing operations: Tailoring P&MA approaches for LMICs
Many companies in these regions are moving beyond at-cost strategies and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives but still lack a systematic approach to P&MA operations, especially in assessing challenges and defining strategies. Below are key P&MA challenges and strategies specific to LMICs:
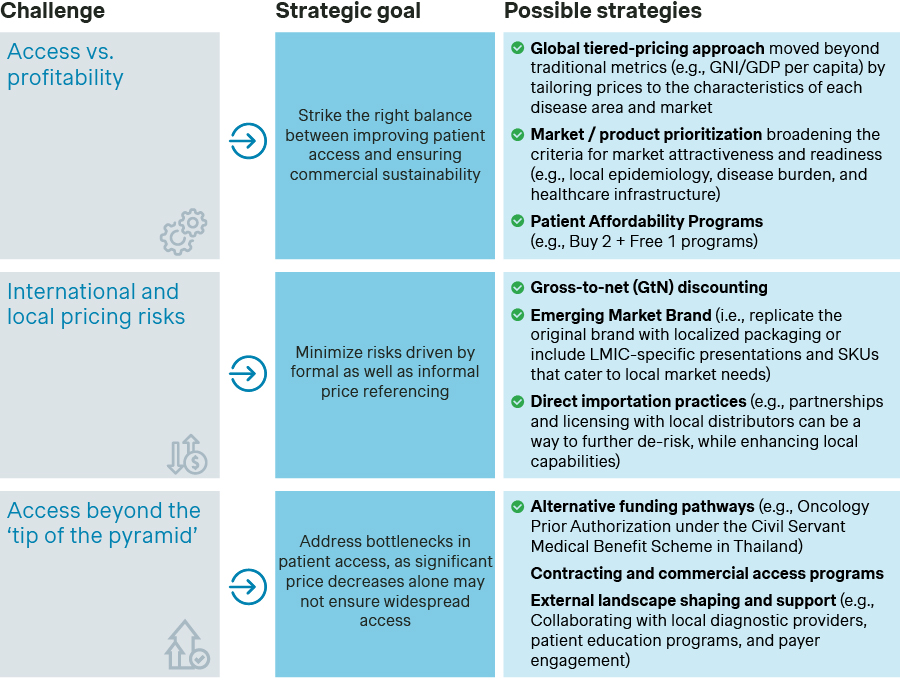
To navigate LMIC dynamics effectively, companies must involve local experts early to identify challenges and shape market-specific strategies. This can be done through external expert discussions or advisory boards, especially when a local presence is not yet established. Additionally, using an archetyping approach - evaluating opportunities and challenges across priority markets within the same archetype - can help manage resource constraints at global and regional levels.
Once a market or group of markets is prioritized, global and regional teams should define clear processes and timelines for effective local execution while addressing constraints like limited resources or absence of a direct local presence. Early, structured external stakeholder engagement is crucial and should start well before P&MA submissions. Companies should engage first with regulatory stakeholders and key opinion leaders, ideally around three years before launch, to establish the necessary market conditions for the asset (e.g., identifying the appropriate clinical data to meet regulatory requirements and clinical expectations). Once their needs are understood and action plans are defined, only then should pharma companies engage P&MA stakeholders before submission.
Building capabilities: Strengthening local P&MA execution
As discussed, successful expansion into LMICs relies on integrating global/regional P&MA expertise with strong local execution. Leading companies create a knowledge database tailored to LMICs, including:
- Stakeholder engagement playbook (tailored to each country and refined by therapeutic area or asset): A guide for engaging local stakeholders, detailing relationship-building timelines and best practices for aligning local partnerships with global/regional objectives.
- Payer value communication pack (asset-specific and adapted to market specifics): A repository of adaptable messaging (e.g., payer value proposition and objection handler), informed by clinical evidence and P&MA strategies, to help local teams communicate the asset's value and tailor it to market conditions and stakeholder needs.
- Market/archetype-specific best practices: Case studies offering insights on successful access models, P&MA negotiations, and overcoming barriers, with continuous updates to reflect evolving market conditions.
Read our article: Equitable access in emerging markets: The next chapter of pharma growth in LMICs
Positioning your P&MA function in the driver's seat: Key takeaways
A P&MA organization steering the course must proactively address each of the four external developments discussed in this article. But readiness doesn't stop there. A future-ready company must also monitor and adapt to other developments specific to their market, portfolio, and corporate strategy.
Pharmaceutical and biotech companies should reassess their P&MA function every 2-3 years to refine their strategic roadmap based on external developments and internal priorities. The roadmap update should cover three core areas: optimizing organizational set-up, enhancing operations, and strengthening team capabilities.
Is your P&MA organization positioned for success? Contact our experts to discuss your priorities and challenges.